22 July 2024
Inflammatory Gum Diseases
Who is a Periodontist?
A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease. Specifically, this field studies the conditions of the soft and hard tissues around the tooth, called the periodontium. Healthy periodontal soft tissues (gums) are pink and tightly attached to the tooth, and in the X-ray image, bone tissue fills the interdental spaces almost completely.
Healthy gums are critical to overall oral health. They form a support for the teeth, protect them, and create a pink aesthetic.
Causes and Symptoms of Inflammatory Periodontal Diseases:
The primary cause of periodontal tissue disease is the presence of soft and hard plaque on the teeth, which results from the activity of microorganisms. The biofilm on the tooth causes inflammation of the gums, which is called gingivitis. If not treated in time, the process can develop into periodontitis, a more severe, destructive, and irreversible form of gum disease, which ultimately leads to tooth decay and loss. The course of periodontitis is greatly influenced by the patient's general condition and systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, etc.).
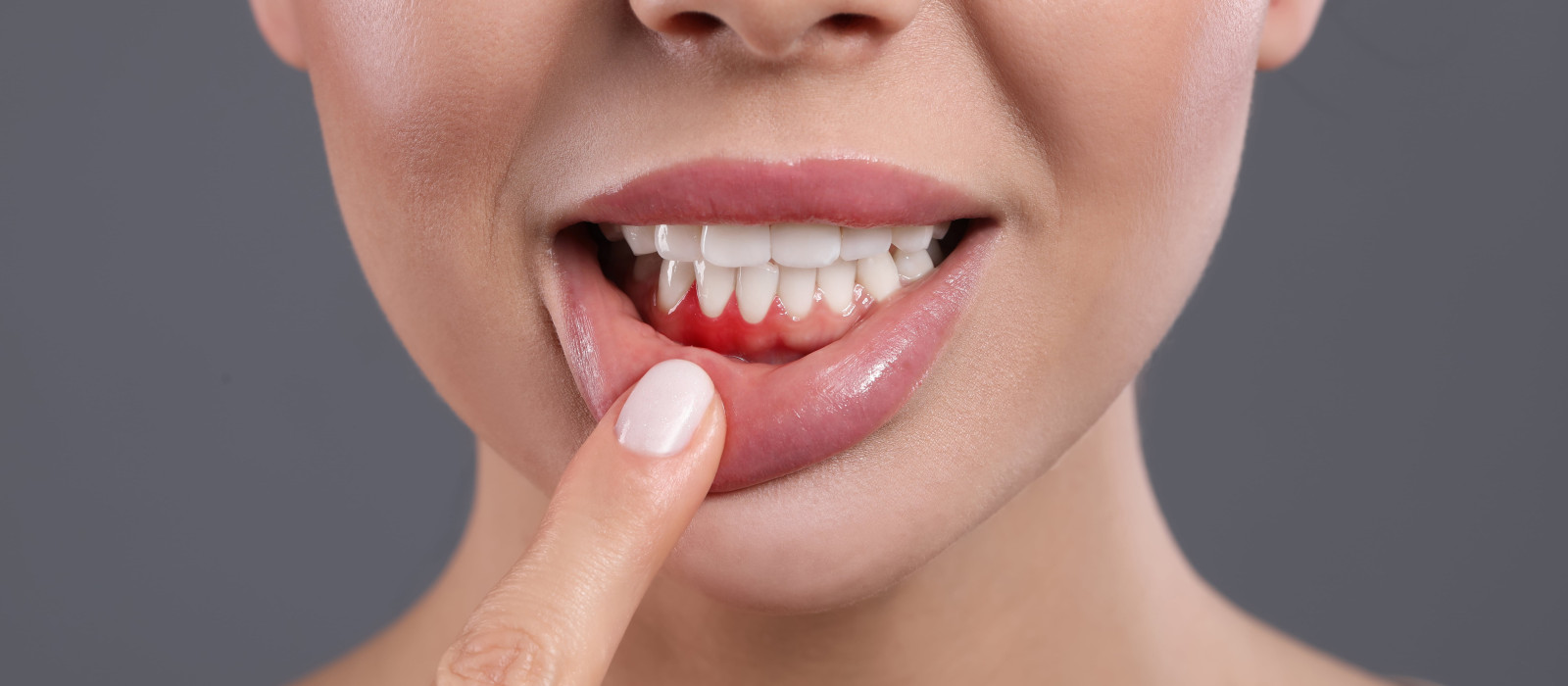
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Gum recession
- Tooth movement and displacement
Treatment and Prevention:
Treatment of inflammatory periodontal disease varies depending on its severity. In the early stages, professional cleaning and improved oral hygiene may be sufficient. More advanced cases may require root instrumentation, medical and/or surgical intervention, along with professional cleaning.
Prevention is key in periodontology. Regular examination of the oral cavity by a periodontist, selection of individual hygiene methods, and a healthy diet are essential. It is recommended to visit a periodontist once every six months for prevention.
Wish you good health and a beautiful smile!
